Hole target detection and location of complex workpiece based on binocular vision
-
摘要:
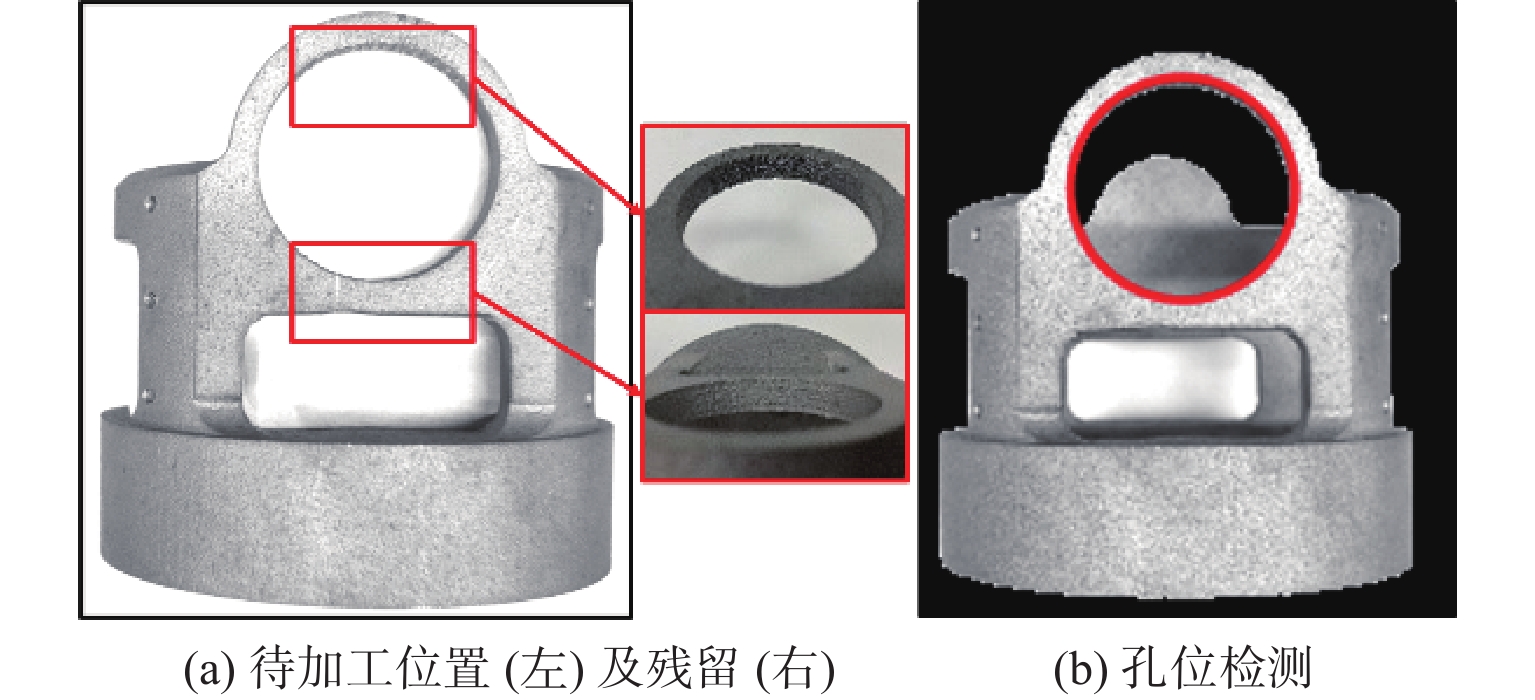
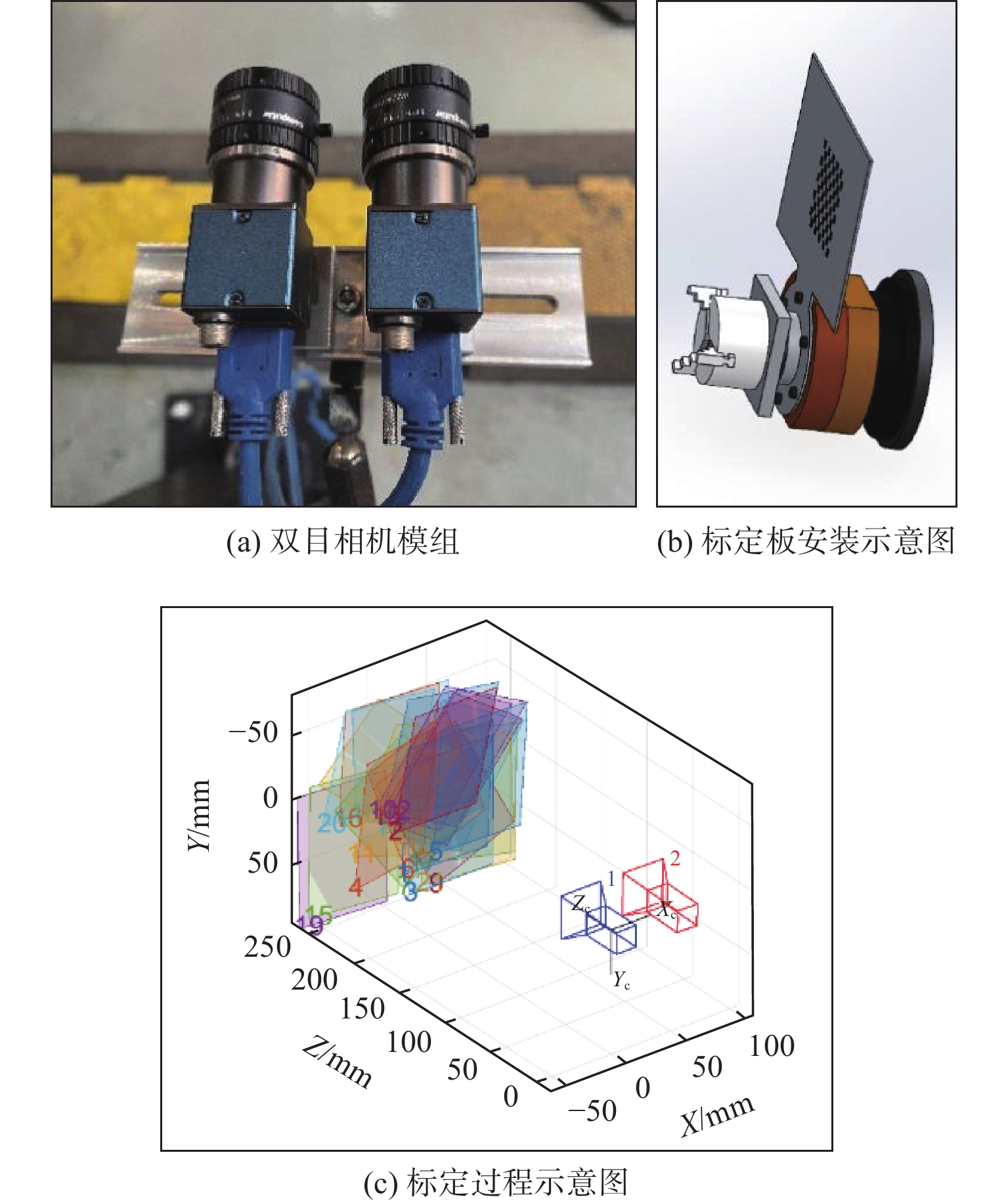
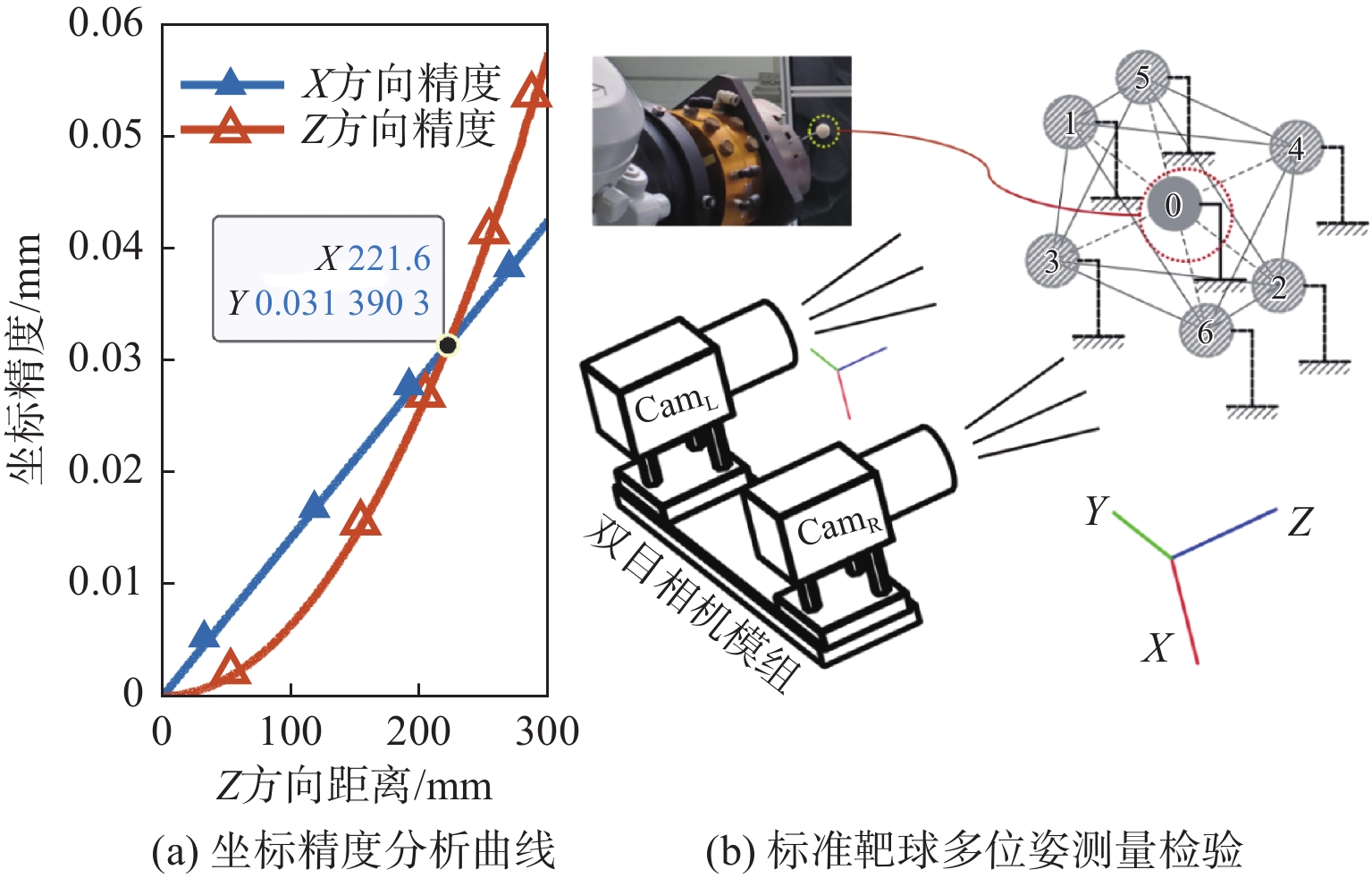
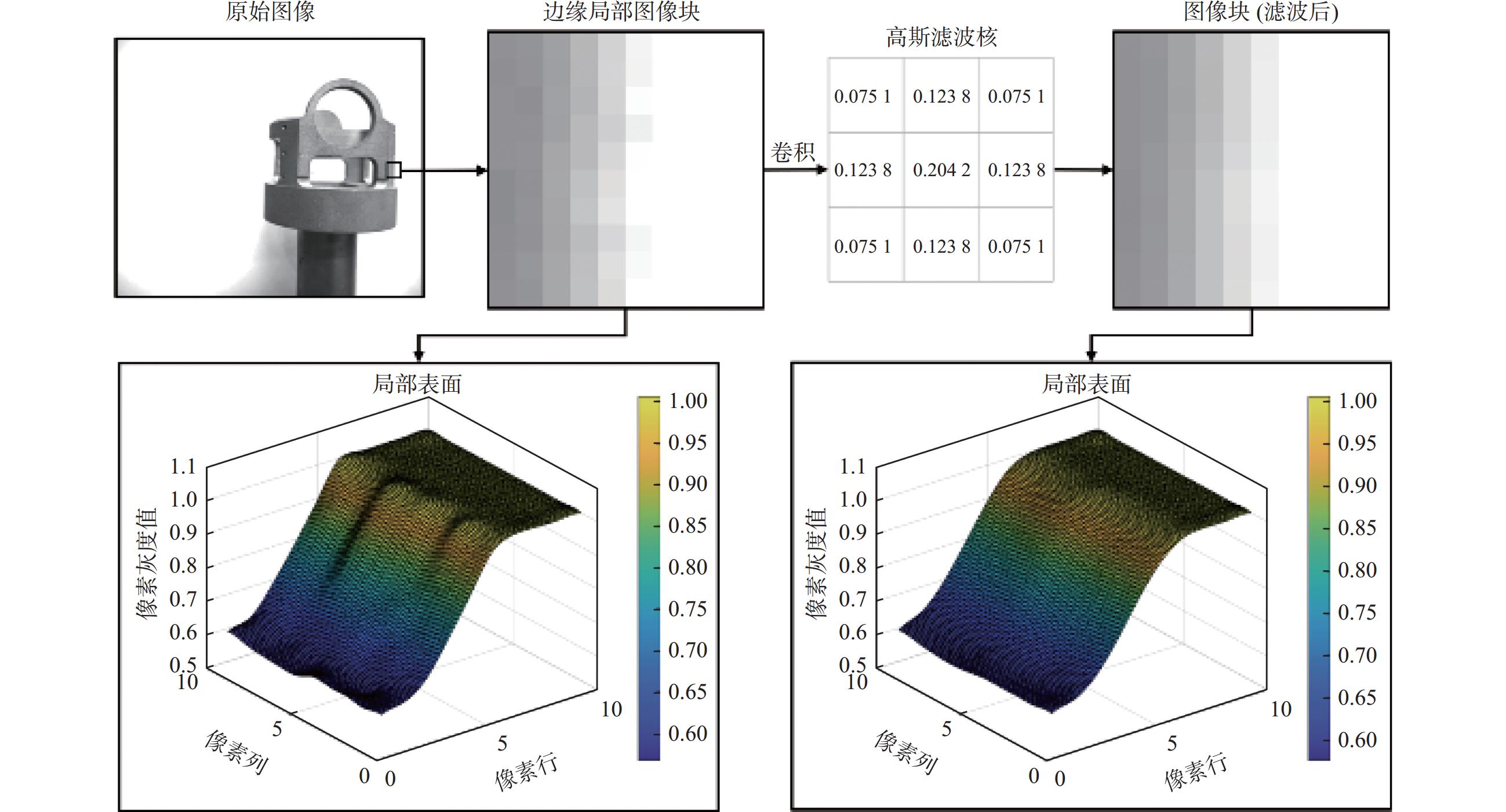
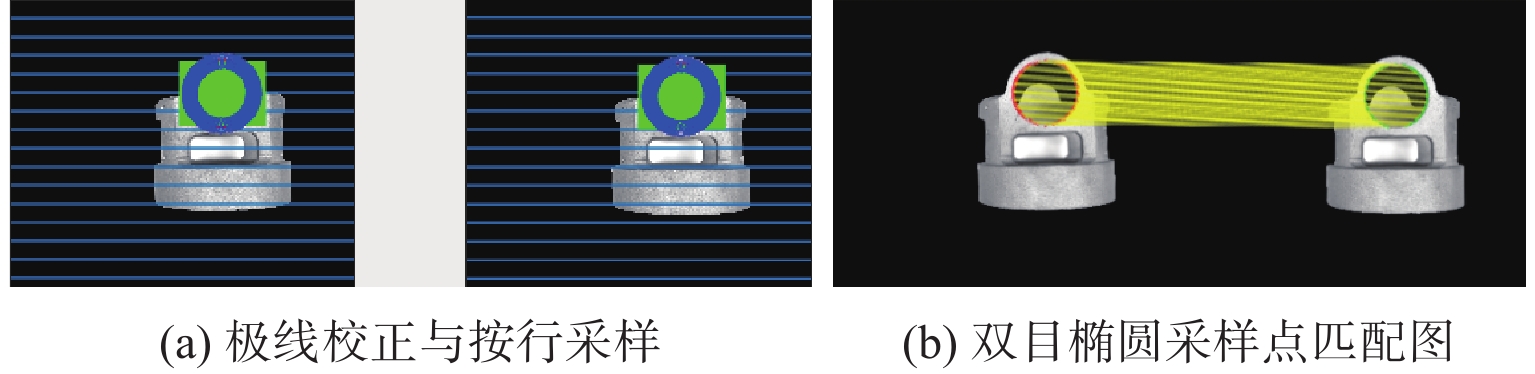
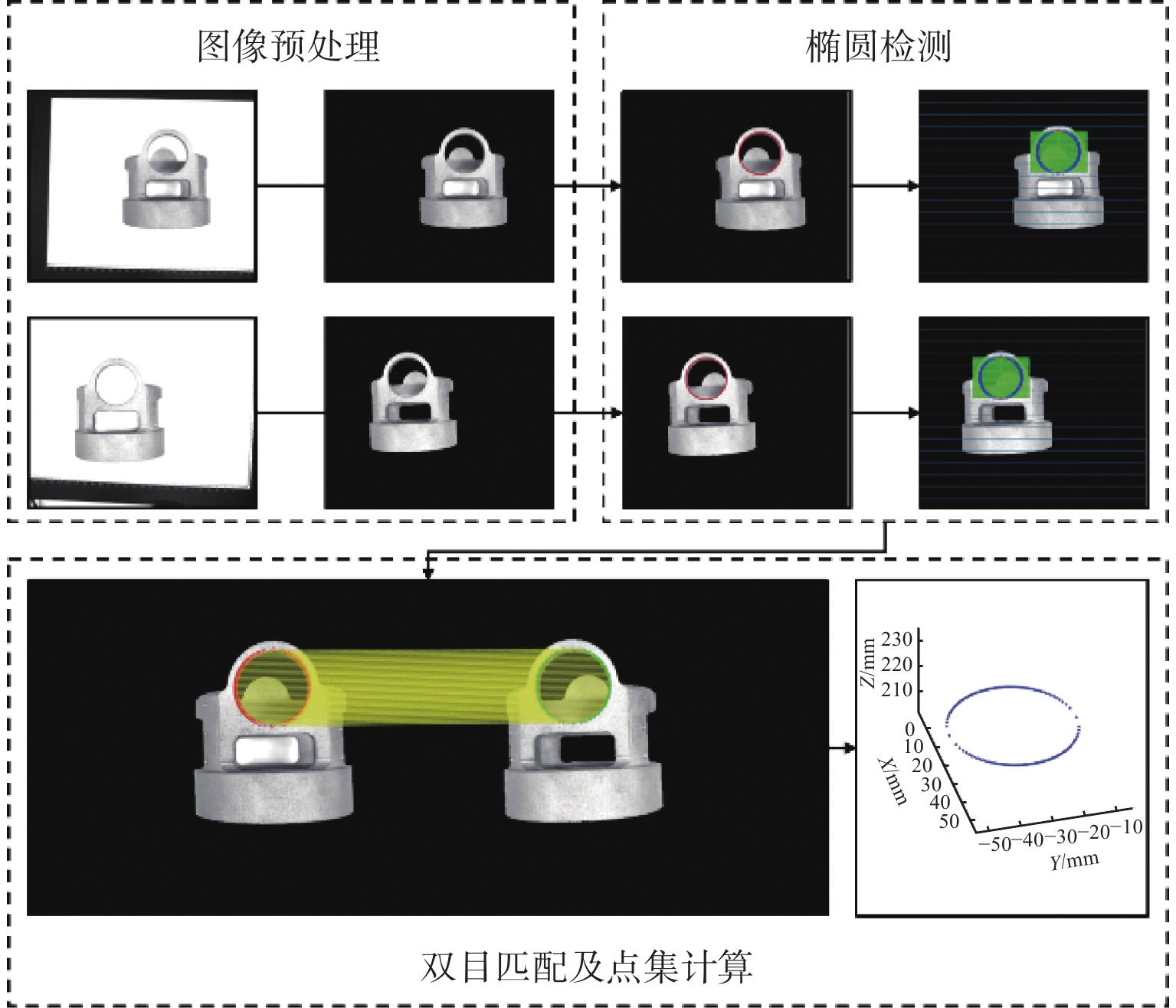
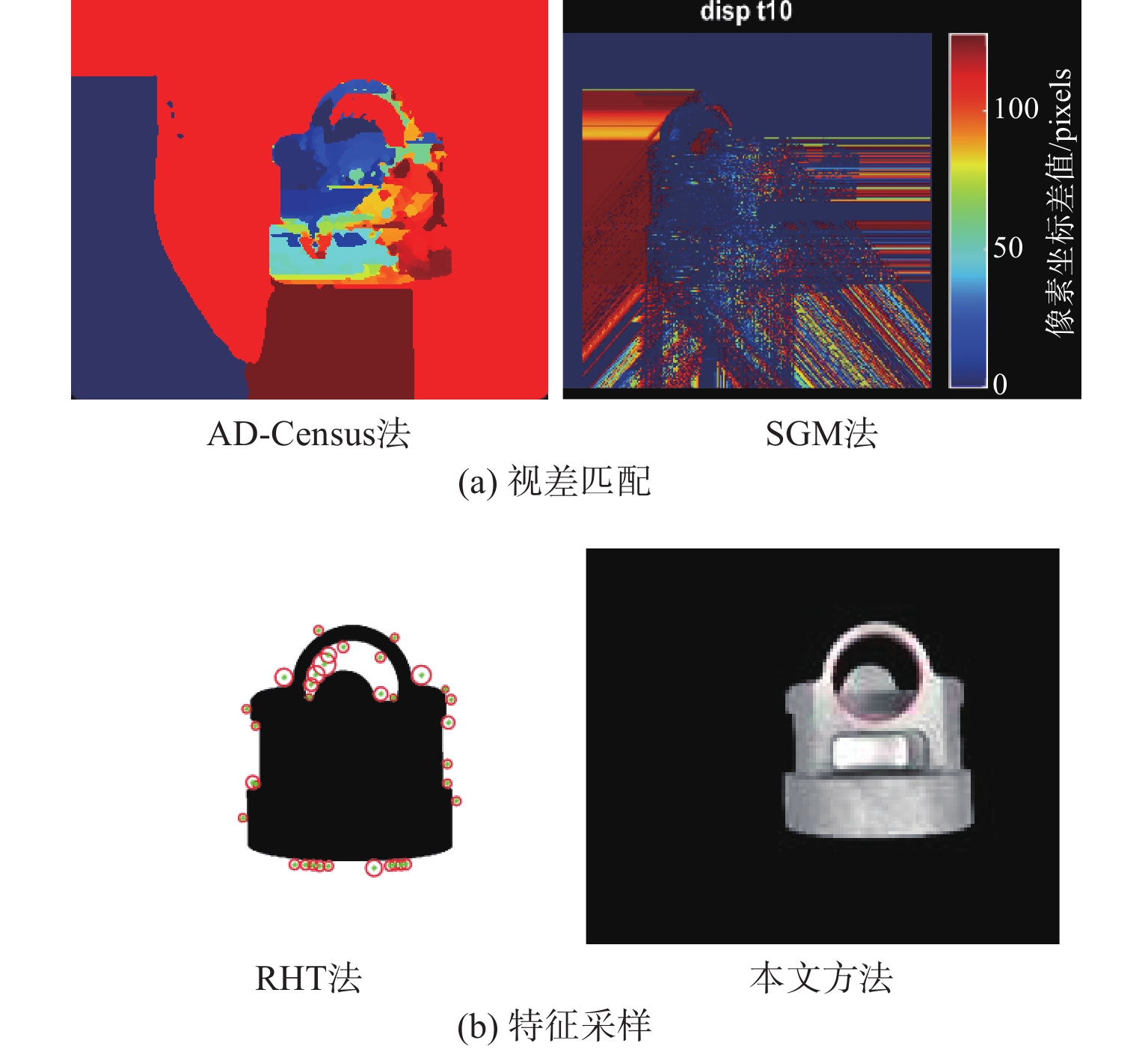
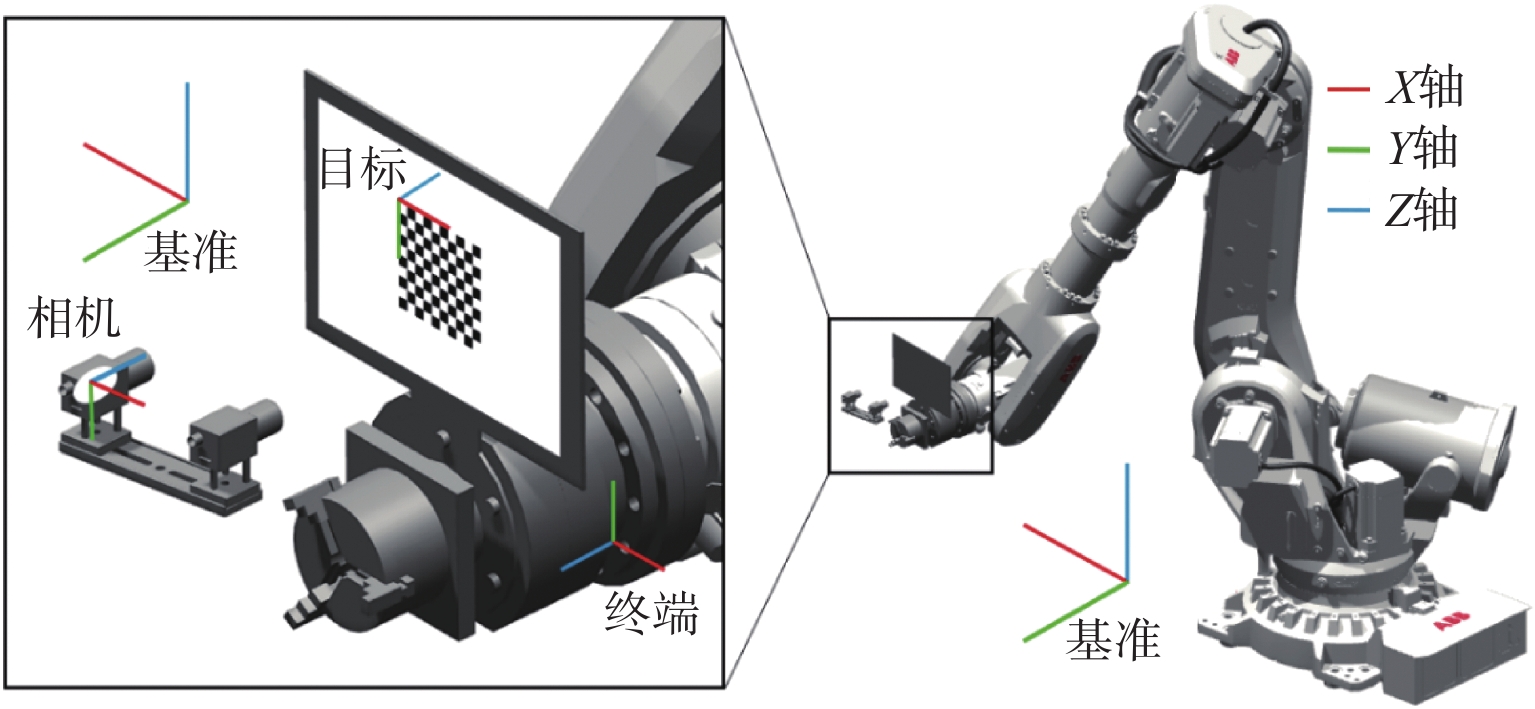
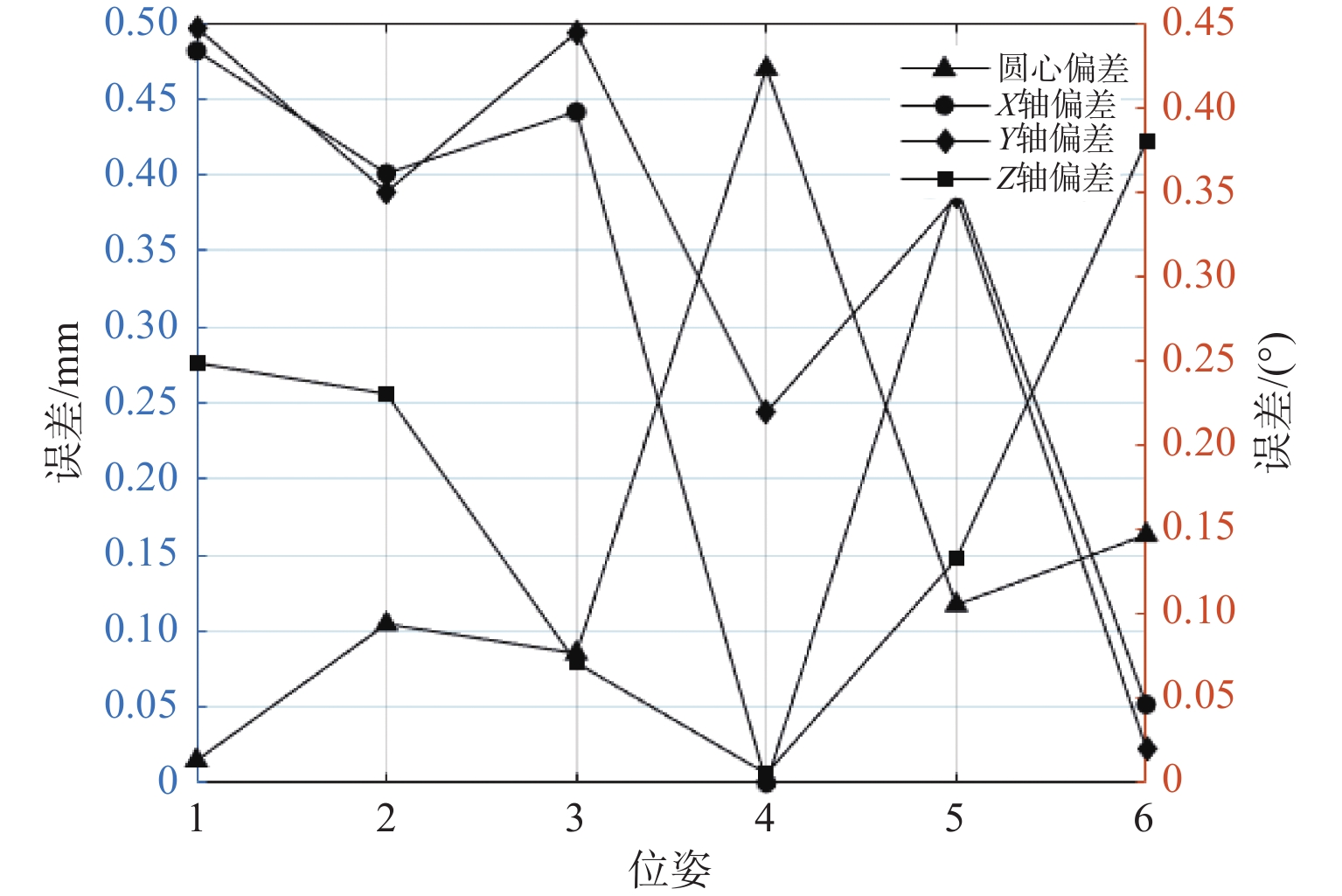
针对金属3D打印件孔洞部位支撑残留后处理问题,提出了一种双目视觉检测定位方法。测量系统基于弧段椭圆识别算法进行工件孔位检测,通过计算待加工孔位在双目模组主相机光心坐标系中的位姿、并将该位姿转换到加工现场机械臂基坐标系,为离线编程和自动加工提供坐标信息。首先标定双目相机并检验硬件系统对标定角点的测量精度;然后对复杂工件的待加工位置椭圆特征进行提取,基于极线校正后图像对左右图椭圆进行同行像素点采集和双目匹配;最终根据多视图原理进行匹配点对的坐标计算,进而输出带有坐标信息的空间圆环。对双目相机模组进行了标定靶球测量验证实验,结果显示尺寸测量误差小于0.20 mm。对实际工件进行了测量定位实验,结果表明,该系统测量圆孔尺寸的最大误差小于0.84%,圆心空间位置误差小于0.50 mm,圆环姿态最大误差小于0.5°。
Abstract:A binocular vision detection and positioning method was proposed to solve the problem of post-processing of hole support residue in metal 3D printing parts. The hole position of the workpiece was detected by the measuring system based on the arc ellipse recognition algorithm. By calculating the pose of the hole position to be machined in the optical center coordinate system of the main camera in binocular module, and converting the pose to the base coordinate system of the robot arm on machining site, the coordinate information was provided for off-line programming and automatic machining. Firstly, the binocular camera was calibrated and the measurement accuracy of the hardware system was checked. Then, the position ellipse features of the complex workpiece to be processed were extracted, and the parallel pixel acquisition and binocular matching were carried out for left and right image ellipses based on the pole-corrected images. Finally, the coordinates of matching point pairs were calculated according to the multi-view principle, and the spatial ring with coordinate information was output. A calibration target ball measurement verification experiment was carried out for binocular camera module. The results show that the measurement error is less than 0.20 mm. The measurement and positioning experiment of the actual workpiece was carried out. The results show that the maximum error of the system is less than 0.84%, the error of the center space is less than 0.50 mm, and the maximum error of the attitude of the ring is less than 0.5°.
-
《等离子体光学加工关键技术研究现状》是关于等离子体加工技术的综述文章。等离子体加工技术,是近年来发展起来的先进光学制造技术,具有快速缓解或去除传统光学加工方法导致的表面/亚表面损伤,以及高效、高精度和高分辨率修整光学面形的优势。该文对包括作者所在单位在内的国内外各研究机构在等离子体加工技术涉及的射流特性、界面物化反应、损伤去除机理、去除函数、加工热效应和工艺定位等关键技术研究内容及成果进行了分析,对等离子体的新型光学加工技术进行了介绍。该文条理清晰,收集资料全面,引文文献新颖,对于从事等离子光学加工或其他光学加工工艺技术人员有较大参考价值。
《快速周扫探测系统扫描平台的高精度稳定控制》对扫描平台的高精度稳定控制用于快速周扫探测系统设计与实现进行了研究,指出了扫描平台的控制是系统清晰稳定成像的关键。围绕提高扫描平台的控制精度、抗干扰性以及稳定性等问题展开研究;建立了双向惯性稳定平台数学模型;控制算法上采用了分数阶PID控制器,提出了扫描平台的控制策略,并对控制性能进行了分析与验证。仿真和硬件实验数据均表明,分数阶PID在控制精度和抗扰动能力方面相比传统PID具有明显的优势,具有重要的理论意义和应用价值。
《基于光的反射与折射定律的表述方法推导及应用》介绍推导了光的反射定律和折射定律的矢量、矩阵及四元数3种表述方法,通过Matlab辅助下的计算分析,实现了矢量、矩阵和四元数表述方法在施密特棱镜检验光路的应用,取得了较好的结果,具有一定的借鉴价值。
《基于深度学习的气溶胶荧光光谱识别应用研究》采用激光诱导荧光技术原理,以单光子探测器为核心器件,设计并搭建了一种高效的荧光光谱仪,对于该光谱仪采集的数据,探索了以一维向量和二维矩阵两种输入形式来实现荧光光谱的识别与分类,并研究对比了主成分分析网络、卷积神经网络和全卷积网络等深度学习网络的识别与分类效果。用于空气中高危病原微生物的识别与分类(识别准确率98.05%。),实现对微生物浓度的精准预测(准确率98.97%)。该研究技术先进,具有学术和工程应用价值,对于环境安全具有重要意义。
《大量程激光位移传感器的成像系统设计》为了解决目前国内自主研发的激光位移传感器基准工作距离短和测量范围小的问题,设计了一种适用于远距离测量的大量程激光位移传感器成像光学系统,完成了系统的优化设计和性能分析,重点分析了成像光学系统对测距精度的影响,所得到的的设计方法,对于相关领域设计人员具有一定的参考价值。
《基于自由曲面设计的全景鱼眼光学系统》介绍了一种基于自由曲面设计的全景鱼眼光学系统,为鱼眼光学镜头提供了新的设计思路,提出了xy焦距不同的设计方法,以达到更高的像素利用率。论文参考了非球面加工类和模造玻璃镜片现状等相关文章,在设计时应已经进行了加工性的考虑,应用意义较大。
《面向边缘智能光学感知的航空紧固件旋转检测》提出一种面向边缘智能光学感知的航空紧固件检测方法。该方法将轻量化的旋转检测方法应用到航空紧固件的检测任务中。基于强化语义和优化空间的特征融合机制提升模型的检测性能,将水平检测改进为旋转检测,显著提升检测精度,并且便于紧固件的自动抓取分拣工作。实验结果表明,与传统方法相比,该方法具有更高的检测精度和更少的参数量。
-
表 1 双目相机系统标定参数
Table 1 Calibration parameters of binocular camera system
参数 左相机 右相机 焦距 $ (2\text{ }413.39,\; 2\text{ }408.07) $ $ (2\text{ 447}\text{.07},\;2\text{ }448.61) $ 径向畸变 $( - 0.125{\text{ }}7,0.214{\text{ }}6,0.009{\text{ }}1)$ $( - 0.098{\text{ }}2{\text{ }},0.144{\text{ 8}}, - 0.043{\text{ 3}})$ 切向畸变 $(0.003{\text{ 2}},0.000{\text{ 7}})$ $( - 0.001{\text{ 5}},0.000{\text{ 9}})$ 旋转矩阵 $\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{r}} {0.999\;7}&{0.021\;5}&{ - 0.013\;7} \\ { - 0.021\;3}&{0.999\;7}&{0.015\;6} \\ {0.014\;1}&{ - 0.015\;3}&{0.999\;8} \end{array}} \right]$ 平移向量 $ \left[-51.535\text{ 9},-0.027\text{ 3},-0.758\text{ 3}\right] $ 表 2 标准球测量结果
Table 2 Measurement results of criterion sphere
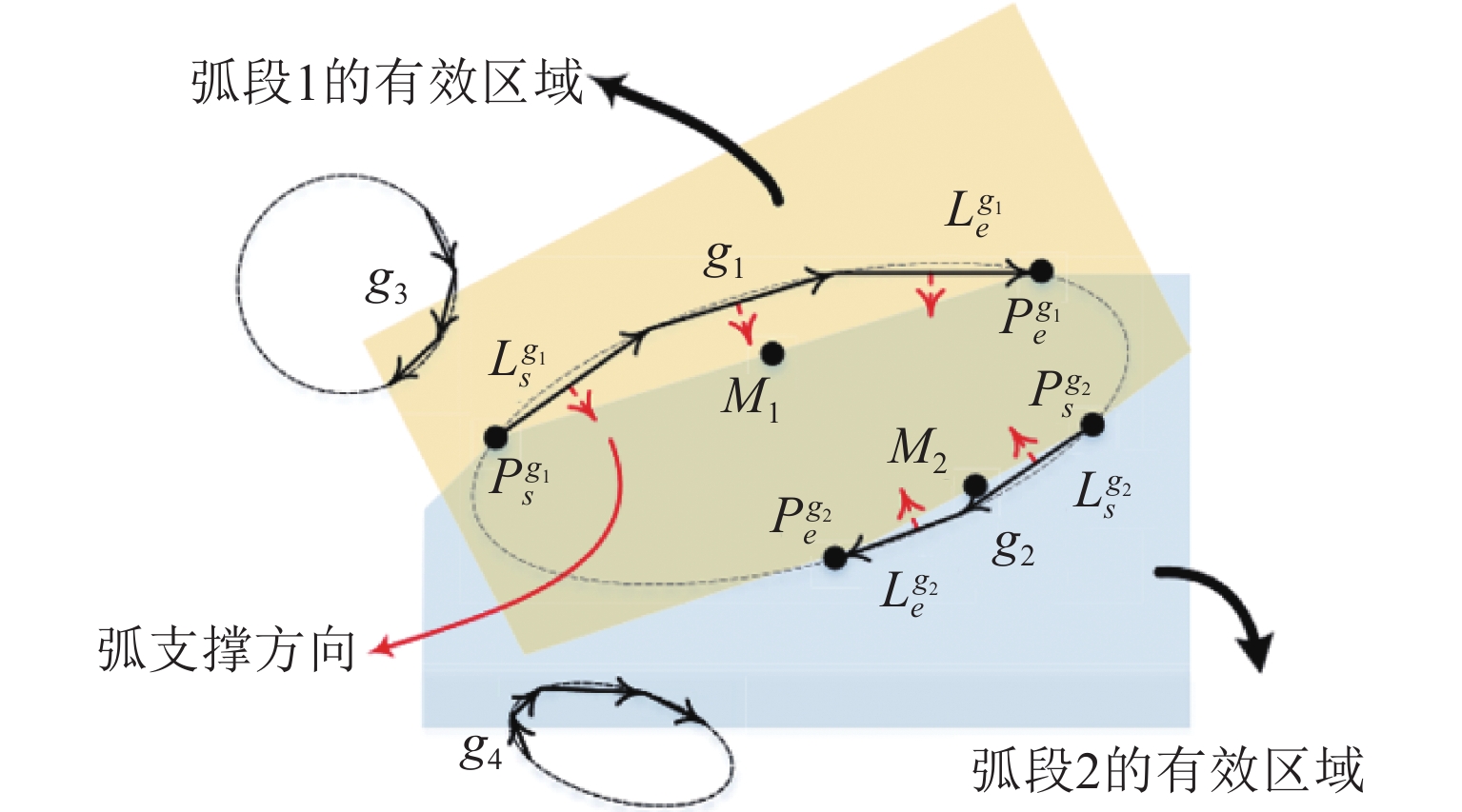
位置序号/参数项 测量结果/mm 偏差(绝对值)/mm 0 20.008 0.020 1 20.151 0.162 2 19.869 0.119 3 20.171 0.183 4 20.116 0.128 5 19.943 0.045 6 20.013 0.025 真值 19.988 mm 最大误差 0.183 mm 均方根误差 0.106 mm 算法1 弧支持组形成过程伪代码 输入:弧支撑线段集${T_l}$;生成线段的圆弧支撑区域${T_r}$;包容角度$\alpha $;线段使用状态参数$S$ 1: 初始化:$G = \emptyset $; 2: 循环: 3: || 从${T_l}$中选择${l_i}$,选择条件:$S({l_i}) \ne used$;设定:${g_{head}} = \emptyset $,${g_{tail}} = \emptyset $,${l_i} \Rightarrow $线段${l_s}$的晶核; 4: || 循环: 5: || | 在${l_s}$的头端搜索连续的弧支撑线段; 6: || | 从搜索结果中排除:$S = used$,到${l_s}$的角度偏差超过$2\alpha $; 7: || | 计算${l_s}$头端的统计面积,使用${T_r}$获得票数最高的线段${l_k}$; 8: || | 刷新:${g_{head}} = {g_{head}} \cup {L_k}$,$S({l_k}) = used$,${l_s} = {l_k}$; 9: || 直到:${l_s} = \emptyset $; 10: || 设定:${l_i} \Rightarrow $线段${l_s}$的生长核;在${l_s}$的尾部重复上述搜索过程即可得到${g_{tail}}$; 11: || ${g_{head}} = \{ {L_{h1}}, \cdots ,{L_{hn}}\} $,${g_{tail}} = \{ {L_{t1}}, \cdots ,{L_{tn}}\} $$ \Rightarrow g = \{ {L_{tn}}, \cdots ,{L_{t1}},{L_i},{L_{h1}}, \cdots ,{L_{hn}}\} $ 12: || 刷新:$G = G \cup g$,$S({l_i}) = used$; 13: 直到:遍历所有弧支撑线段; 14: 返回:$G$; 输出:弧支撑群$G$ 表 3 工件位姿初值
Table 3 Initial values of workpiece pose
圆心坐标/mm 法向量夹角/($^\circ $) X轴 Y轴 Z轴 $[22.60, - 33.25,216.62]$ $88.13$ $88.50$ $2.40$ -
[1] 杨鑫, 王婉琳, 范亚卓, 等. 3D打印金属零件后处理研究现状[J]. 功能材料, 2020, 51(5): 5043-5052 YANG Xin, WANG Wanlin, FAN Yazhuo, et al. Research status of post-processing of 3D printing metal parts[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2020, 51(5): 5043-5052.
[2] 朱福康, 刘毅, 孟凡杰, 等. 基于图像深度信息集的Hough圆检测方法[J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术, 2018(5): 85-88. ZHU Fukang, LIU Yi, MENG Fanjie, et al. Hough circles detection based on depth information set of image[J]. Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique, 2018(5): 85-88.
[3] 罗哉, 赵洪楠, 江文松, 等. 基于线激光扫描的基准孔检测与定位方法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2021, 42(12): 184-190. LUO Zai, ZHAO Hongnan, JIANG Wensong, et al. A detection and positioning method for the base hole based on line laser scanning[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2021, 42(12): 184-190.
[4] 姜春英, 闫子龙, 牛祥鑫, 等. 基于局部主动轮廓模型的飞机壁板铆接孔定位方法研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2019, 62(10): 58-63. JIANG Chunying, YAN Zilong, NIU Xiangxin, et al. Research on positioning method of aircraft panel riveting hole based on local active contour model[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 62(10): 58-63.
[5] 张太恒, 梅标, 乔磊, 等. 纹理边界引导的复合材料圆孔检测方法[J]. 浙江大学学报 (工学版), 2020, 54(12): 2294-2300. ZHANG Taiheng, MEI Biao, QIAO Lei, et al. Detection method for composite hole guided by texture boundary[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2020, 54(12): 2294-2300.
[6] HO C C, ZHANG R H. Machine vision-based relative-angle measurement system between circular holes[J]. Measurement and Control, 2021, 54(5/6): 647-657.
[7] LI D H, NAN F, XUE T, et al. Circle detection of short arc based on randomized Hough transform[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA). Takamatsu: IEEE, 2017: 258-263.
[8] CHEN S L, XIA R B, ZHAO J B, et al. A hybrid method for ellipse detection in industrial images[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 68: 82-98. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.03.007
[9] CAKIR H I, BENLIGIRAY B, TOPAL C. Combining feature-based and model-based approaches for robust ellipse detection[C]//2016 24th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO). Budapest: IEEE, 2016: 2430-2434.
[10] HASAN S F, SADAT R M N, RAHMAN M A, et al. A precise and low complexity distance and size measurement of circular objects from camera position using still images[C]//2006 International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering. Dhaka: IEEE, 2006: 439-442.
[11] LU C S, XIA S Y, SHAO M, et al. Arc-support line segments revisited: an efficient high-quality ellipse detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 768-781. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2934352
[12] MEI X, SUN X, ZHOU M C, et al. On building an accurate stereo matching system on graphics hardware[C]//2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops). Barcelona: IEEE, 2011: 467-474.
[13] ROTHER C, KOLMOGOROV V, BLAKE A. GrabCut: interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts[M]//Seminal graphics papers: pushing the boundaries: Volume 2. New York: ACM, 2023: 593-598.
[14] 理查德·哈特利, 安德鲁·西塞曼. 计算机视觉中的多视图几何[M]. 韦穗, 杨尚骏, 章权兵, 等, 译. 2版. 合肥: 机械工业出版社, 2019: 211-214. RICHARD H, ANDREW Z. Multiple view geometry in computer vision[M]. WEI S, YANG S J, ZHANG Q B, et al, Transl. 2nd ed. Hefei: Machinery Industry Press, 2019: 211-214.
[15] 李英硕, 杨帆, 袁兆奎. 空间圆形拟合检测新方法[J]. 测绘科学, 2013, 38(6): 147-148. LI Yingshuo, YANG Fan, YUAN Zhaokui. A detection method for 3D circle fitting[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2013, 38(6): 147-148.



 下载:
下载:
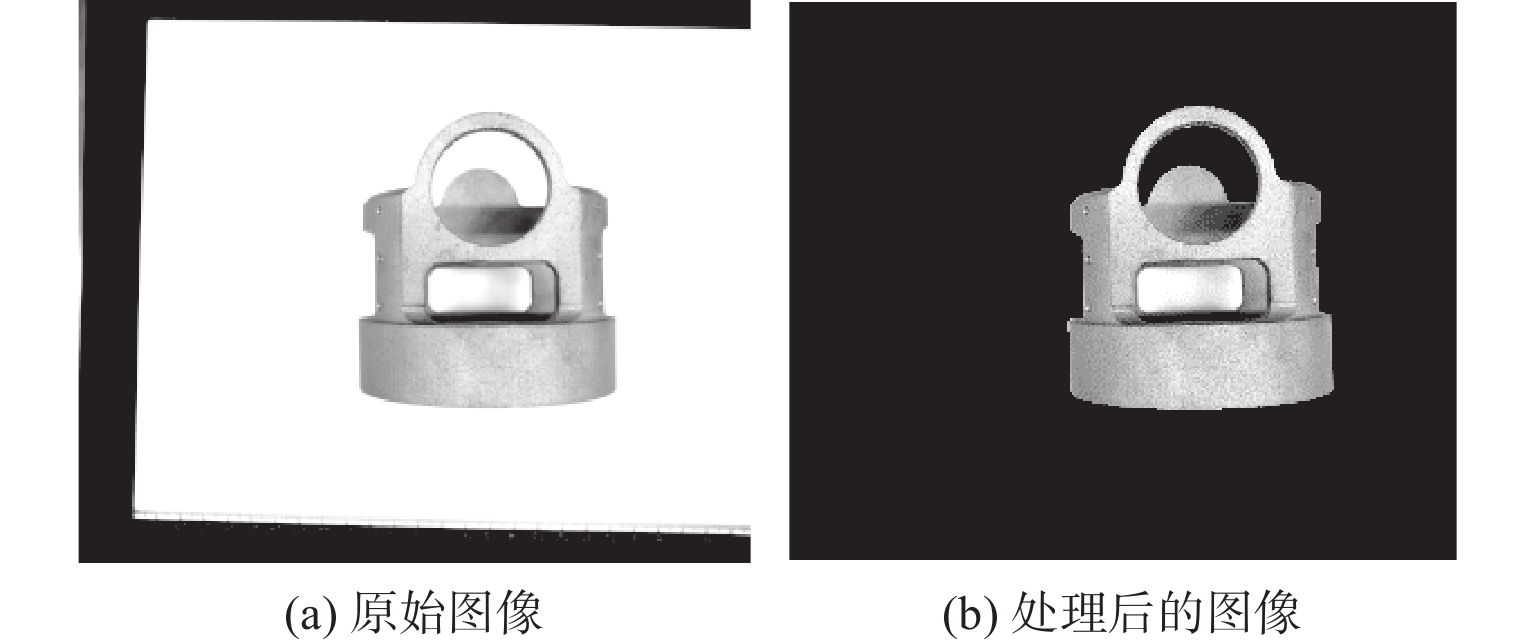
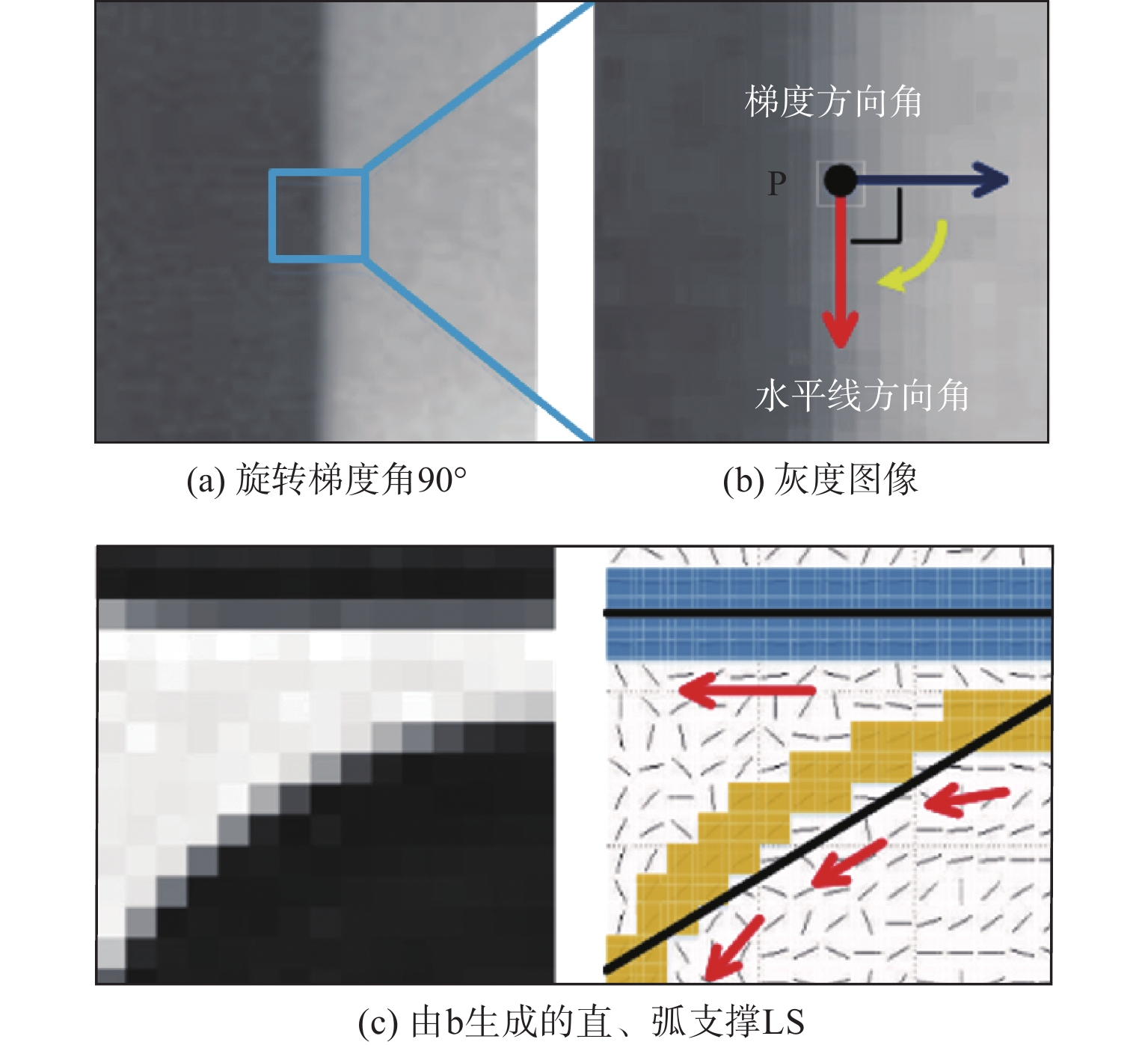
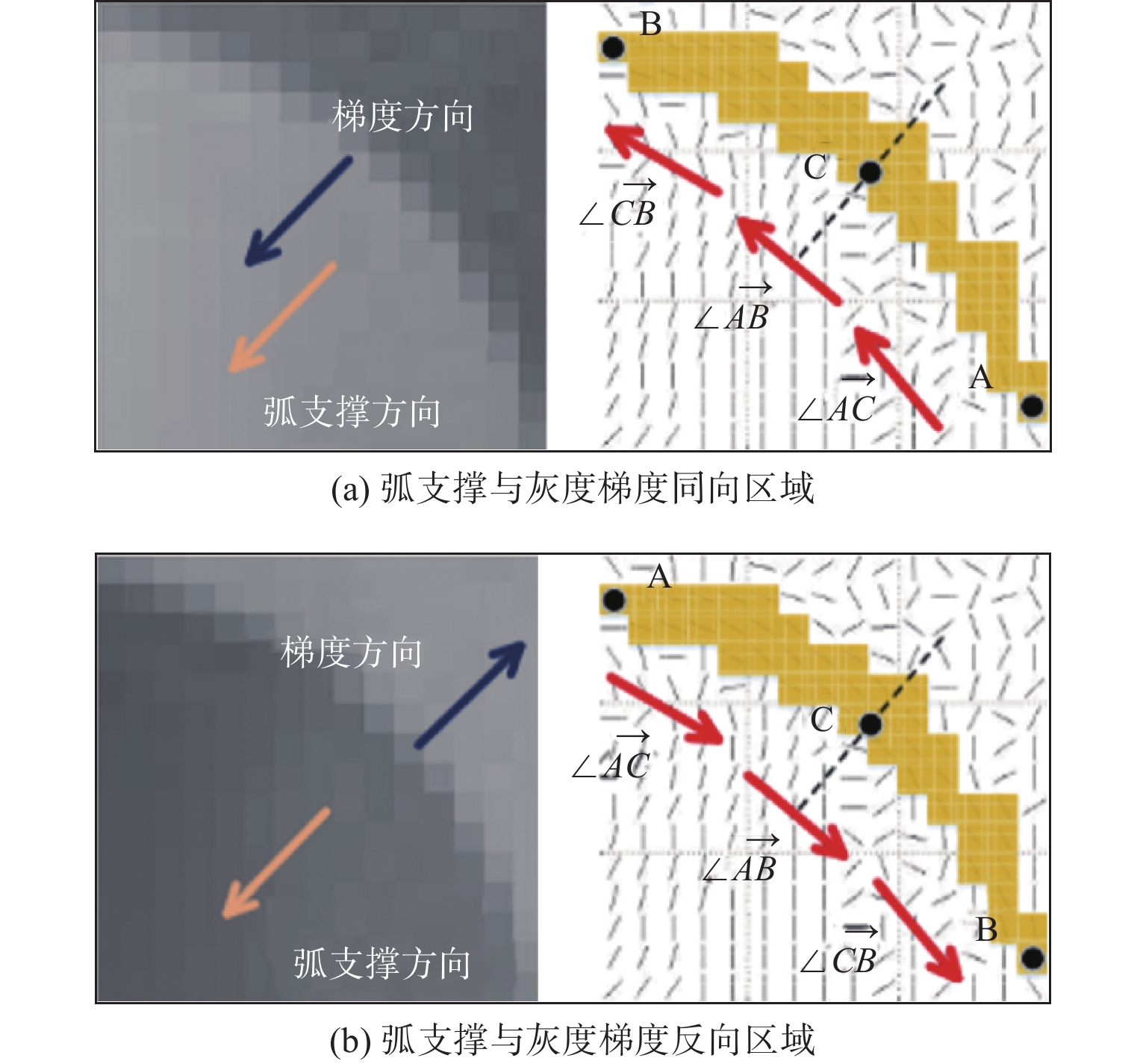
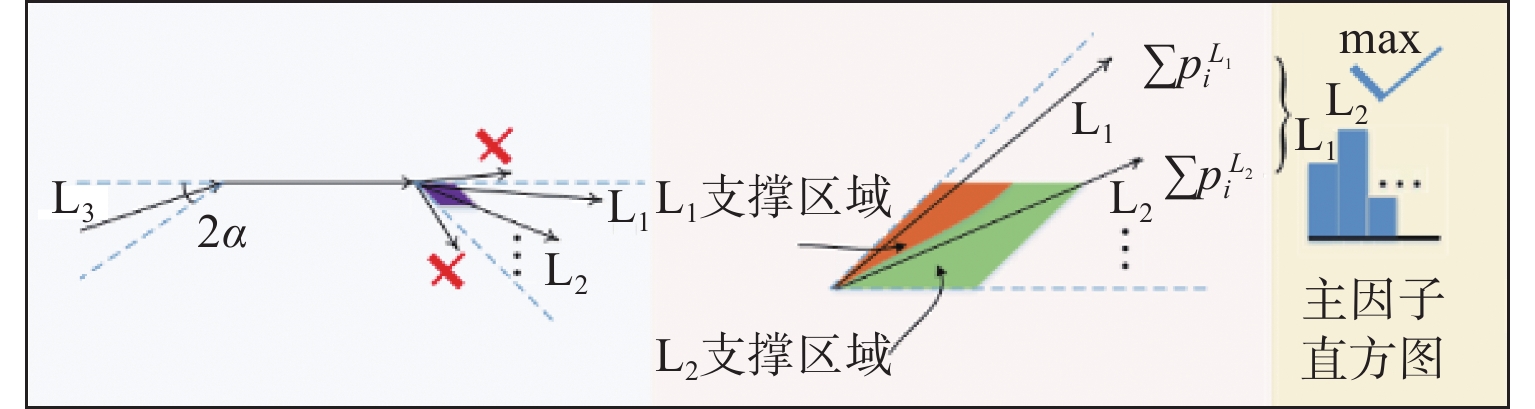



 陕公网安备 61011302001501号
陕公网安备 61011302001501号 